Christopher J. Sweeney, MD, MBBS, presented “Overview of Treatment for Advanced Prostate Cancer, including Metastatic Disease – Novel Treatment” during the 4th Global Summit on Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer on October 3, 2019 in Boston, Massachusetts.
How to cite: Sweeney, Christopher J. “Overview of Treatment for Advanced Prostate Cancer, including Metastatic Disease – Novel Treatment” October 3, 2019. Accessed Jun 2025. https://grandroundsinurology.com/overview-of-treatment-for-advanced-prostate-cancer-including-metastatic-disease-novel-treatment/
Overview of Treatment for Advanced Prostate Cancer, including Metastatic Disease – Novel Treatment – Summary:
Christopher Sweeney, MD, MBBS, gives an overview of the most promising research into novel treatments for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), focusing on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3Kinase)/Akt inhibition, Poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors, and lutetium-labeled prostate-specific membrane antigen (Lu-PSMA). He emphasizes the importance of careful patient selection for these therapies, and suggests that future studies should focus on combination therapies and avoid duplicative research.
Abstract:
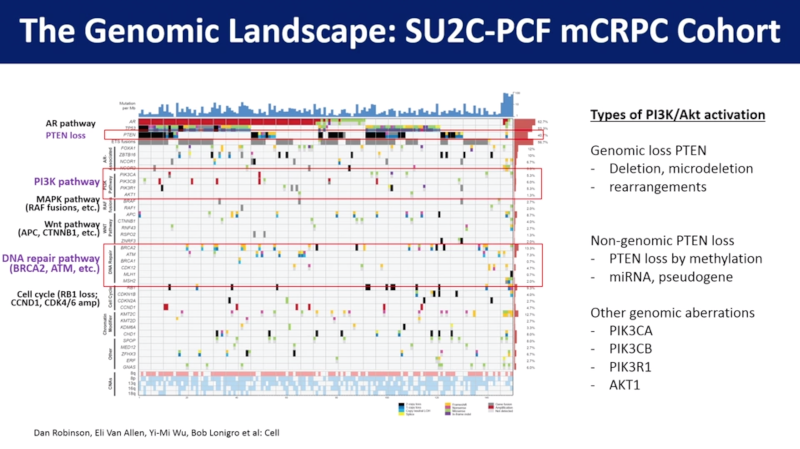
The genetic landscape of prostate cancer has been well-mapped in recent years, and the discovery of the vast array of mutations that can occur in mCRPC has led many researchers to try and determine if any are actionable. Novel therapies currently in development include androgen receptor inhibitors, epigenetic modulators, cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors, and various immunotherapies, but researchers looking at PI3Kinase/Akt inhibition, PARP inhibitors, and Lu-PSMA have presented the most promising data so far.
The PI3Kinase/Akt pathway is a key signaling pathway in prostate cancer and is viewed as a high-yield target. The most promising study in this area found that patients who have PTEN loss who got abiraterone with an Akt inhibitor had a markedly improved time to radiographic progression. Another study showed that these hormonal therapies are less likely to work if a patient has detectable, circulating ARv7. PARP inhibitors have also shown some promise but, again, only in patients with specific mutations. BRCA1 and 2 have proven particularly actionable. In the area of radioligand therapy, one mCRPC patient treated with Lu-PSMA saw a complete PSMA-PET radiographic response and a massive decrease in PSA. A promising study into Lu-PSMA has also found a substantial and prolonged response in some carefully-selected (not PSMA-PET negative) patients.
Once a greater body of research is acquired, these novel treatments may become standard of care for the specific kinds of patients they are shown to benefit. Rigorous phase 3 trials are still needed, though. As researchers continue to look for treatments based on the genomics of mCRPC, they could consider investigating combination therapies as well as seeking out new target opportunities. It is important to avoid duplicating research and over-investing in just one or two areas.
About The 4th Global Summit on Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer:
The Global Summit on Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer is a multi-day, multi-disciplinary forum dedicated to informing healthcare stakeholders about topics including in-vitro fluid- and tissue-based molecular diagnostics, novel observation strategies such as active surveillance, and novel therapeutic interventions. Along with this forum’s efforts to form a consensus on the future of prostate diagnostics and precision care, it aims to create an educational and research strategy for its realization. Dr. Sweeney presented this lecture during the 4th iteration of this Summit in 2019.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR
Christopher J. Sweeney, MBBS, is a Medical Oncologist at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, Massachusetts, and Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. He received his medical degree from the University of Adelaide in Australia, and then completed an internship at the Royal Adelaide Hospital. Dr. Sweeney did his residency in internal medicine at Gundersen Lutheran Medical Center in La Crosse, Wisconsin. He went on to complete a Fellowship in Hematology/Oncology at Indiana University Medical Center in Indianapolis, where he was later appointed Associate Director for Clinical Research for the Simon Cancer Center. Dr. Sweeney joined the Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology at DFCI and Harvard Medical School in 2009. His primary research interest is drug discovery and development. His academic focus is primarily on the management of genitourinary malignancies, with a focus on prostate and testicular cancer.
